|
What is a slope stability analysis?
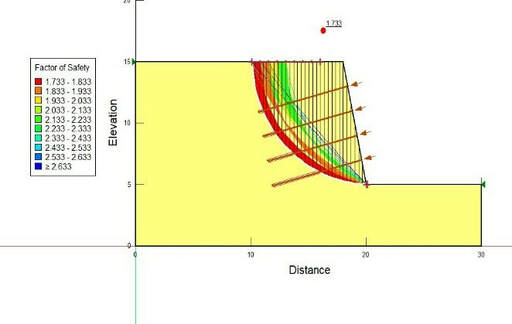
The slope stability analyses in geotechnical engineering have followed closely the developments in soil and rock mechanics as a whole. Slopes either occur naturally or are engineered by humans. Slope stability problems have been faced throughout history when men and women or nature has disrupted the delicate balance of natural soil slopes. Furthermore, the increasing demand for engineered cut and fill slopes on construction projects has only increased the need to understand analytical methods, investigative tools, and stabilization methods to solve slope stability problems. Slope stabilization methods involve specialty construction techniques that must be understood and modelled in realistic ways. An understanding of geology, hydrology, and soil properties is central to applying slope stability principles properly. Analyses must be based upon a model that accurately represents site subsurface conditions, ground behavior, and applied loads. Judgments regarding acceptable risk or safety factors must be made to assess the results of analyses. Various methods used for slope stability analysis are: Limit equilibrium method, slice method, Fellinius method, Bishop method, Janbu Method, Bell method, Spencer method, Morgenstern Price Method. What kinds of software can aid in slope stability analysis? Slope stability procedures are well suited to computer analysis due to the interactive nature of the solution. Also, the simplified hand solution procedures do not properly account for interslice forces, irregular failure surfaces, seismic forces, and external loads such as line load surcharges or tieback forces. Several user-friendly computer programs exist to analyse two-dimensional slope stability problems. One of the advantages of a computer program is that it allows parametric studies to be performed by varying parameters of interest, e.g., shear strength parameters. More complex computer programs are available for three-dimensional slope stability analysis. As a minimum, a basic two-dimensional slope stability program is recommended for routine use. slope stability programs such as the ReSSA (2001), SLOPE/W, SLIDE, STABL series, most popular software to be used is SLOPE/W, GEO5, PLAXIS etc. These software products basically give a 'factor of safety' to be used for the design purpose. Using the specific method all the analysis is done and design procedure is carried out. |
What is the purpose of a slope stability analysis?
In most applications, the primary purpose of slope stability analysis is to contribute to the safe and economic design of excavations, embankments, earth dams, landfills, and spoil heaps. Slope stability evaluations are concerned with identifying critical geological, material, environmental, and economic parameters that will affect the project, as well as understanding the nature, magnitude, and frequency of potential slope problems. When dealing with slopes in general and slope stability analysis in particular, previous geological and geotechnical experience in an area is valuable. The aims of slope stability analysis are...
What causes slope failure? Slope failure occurs when the downward movements of material due to gravity and shear stresses exceeds the shear strength. Therefore, factors that tend to increase the shear stresses or decrease the shear strength increase the chances of failure of a slope. Different processes can lead to reduction in the shear strengths of rock mass. Increased pore pressure, cracking, swelling, decomposition of clayey rock fills, creep under sustained loads, leaching, strain softening, weathering and cyclic loading are common factors that decrease the shear strength of rock mass. In contract to this the shear stress in rock mass may increase due to additional loads at the top of the slope and increase in water pressure in cracks at the top of the slope, increase in soil weight due to increased water content, excavation at the bottom of the slope and seismic effects. |
- Welcome
- PORTFOLIO
-
Services
-
Geotechnical Engineering
>
- Geotechnical Explorations >
-
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
>
- GEOLOGICAL ENGINEERING >
- Septic Engineering >
- PHASE I-III ASSESSMENTS
- ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENTS >
- Site-Specific Seismic Evaluations >
- BUILDING ASSESSMENTS >
- Retaining Walls
- Shoring
- Pin Piles
- Gabion wall
- HELICAL PIER
- Structural Retrofitting
- MANTA RAY ANCHORS
- GEOPHYSICS
- PAVEMENTS / PUBLIC WORKS >
- SOFTWARE >
-
Geotechnical Engineering
>
- Contact Us
- Employment
- Library
- Florida Geo Services
- Blog
- Landing 2024
- Welcome
- PORTFOLIO
-
Services
-
Geotechnical Engineering
>
- Geotechnical Explorations >
-
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
>
- GEOLOGICAL ENGINEERING >
- Septic Engineering >
- PHASE I-III ASSESSMENTS
- ENVIRONMENTAL ASSESSMENTS >
- Site-Specific Seismic Evaluations >
- BUILDING ASSESSMENTS >
- Retaining Walls
- Shoring
- Pin Piles
- Gabion wall
- HELICAL PIER
- Structural Retrofitting
- MANTA RAY ANCHORS
- GEOPHYSICS
- PAVEMENTS / PUBLIC WORKS >
- SOFTWARE >
-
Geotechnical Engineering
>
- Contact Us
- Employment
- Library
- Florida Geo Services
- Blog
- Landing 2024